// 节点区间定义
// [start, end] 代表节点的区间范围
// max 是节点在(start,end)区间上的最大值
// left , right 是当前节点区间划分之后的左右节点区间
public class SegmentTreeNode {
public int start, end, max;
public SegmentTreeNode left, right;
public SegmentTreeNode(int start, int end, int max) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
this.max = max
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
给定一个区间,我们要维护线段树中存在的区间中最大的值。这将有利于我们高效的查询任何区间的最大值。给出A数组,基于A数组构建一棵维护最大值的线段树,我们可以在O(logN)的复杂度内查询任意区间的最大值:
比如原数组A = [1, 4, 2, 3]
线段树的建立
举一反三:
如果需要区间的最小值:
root.min = Math.min(root.left.min, root.right.min);
如果需要区间的和:
root.sum = root.left.sum + root.right.sum;
1. 如何更好的查询Query
构造线段树的目的就是为了更快的查询。
给定一个区间,要求区间中最大的值。线段树的区间查询操作就是将当前区间分解为较小的子区间,然后由子区间的最大值就可以快速得到需要查询区间的最大值。
query(1,3) = max(query(1,1),query(2,3)) = max(4,3) = 4
上述例子将[1, 3]区间分为了[1, 1]和[2, 3]两个区间,因为[1, 1]和[2, 3]存在于线段树上,所以区间的最大值已经记录好了,所以直接拿来用就可以了。所以拆分区间的目的是划分成为线段树上已经存在的小线段。
2. 如何拆分区间变成线段树上有的小区间:
在线段树的层数上考虑查询 考虑长度为8的序列构造成的线段树区间[1, 8], 现在我们查询区间[1, 7]。
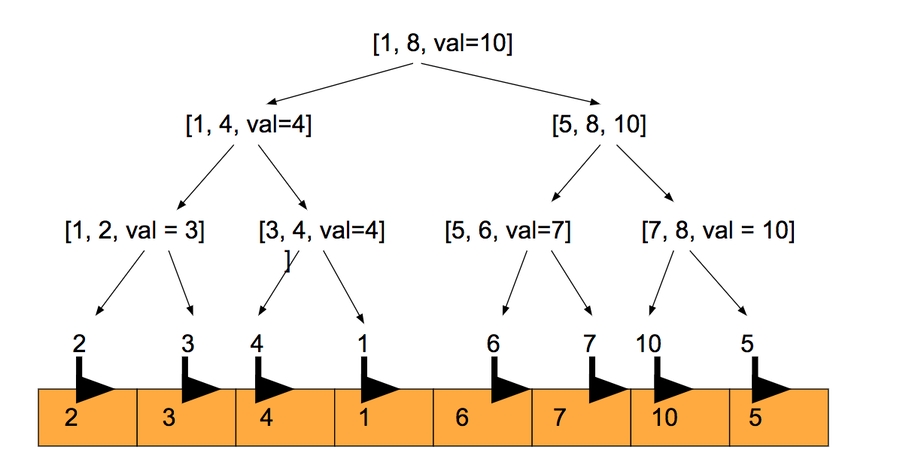
第一层会查询试图查询[1, 7], 发现区间不存在,然后根据mid位置拆分[1, 4]和[5, 7]
第二层会查询[1, 4],[5, 7], 发现[1, 4]已经存在,返回即可,[5, 7]仍旧需要继续拆分
第三层会查询[5, 6],[7, 7], 发现[5, 6]已经存在,返回即可,[7, 7]仍旧需要继续拆分
第四层会查询[7, 7]
任意长度的线段,最多被拆分成logn条线段树上存在的线段,所以查询的时间复杂度为O(log(n))记住就好:)
更新序列中的一个节点,如何把这种变化体现到线段树中去,例如,将序列中的第4个点A[3]更新为5, 要变动3个区间中的值,分别为[3,3],[2,3],[0,3]
提问:为什么需要更新这三个区间?:因为只有这三个在线段树中的区间,覆盖了3这个点。
可以这样想,改动一个节点,与这个节点对应的叶子节点需要变动。因为叶子节点的值的改变可能影响到父亲节点,然后叶子节点的父亲节点也可能需要变动。
如果我们继续把A[2]从2变成4,线段树又该如何更新呢?
线段树变化后的状态为:
如果我们继续把A[1]从4变成3,线段树又该如何更新呢?
线段树变化后的状态为:
更新所以需要从叶子节点一路走到根节点, 去更新线段树上的值。因为线段树的高度为log(n),所以更新序列中一个节点的复杂度为log(n)。
因为每次从父节点走到子节点的时候,区间都是一分为二,那么我们要修改index的时候,我们从root出发,判断index会落在左边还是右边,然后继续递归,这样就可以很容易从根节点走到叶子节点,然后更新叶子节点的值,递归返回前不断更新每个节点的最大值即可。具体代码实现如下:
如果需要区间的最小值或者区间的和,构造的时候同理。
通过前面问题的分析,我们对线段树问题可以做如下总结:
1 如果问题带有区间操作,或者可以转化成区间操作,可以尝试往线段树方向考虑
从面试官给的题目中抽象问题,将问题转化成一列区间操作,注意这步很关键
2 当我们分析出问题是一些列区间操作的时候
我们都可以采用线段树来解决这个问题
3 套用我们前面讲到的经典步骤和写法,即可在面试中完美的解决这些题目!
如果我们删除或者增加区间中的元素,那么区间的大小将发生变化,此时是无法使用线段树解决这种问题的。
