BST to Doubly LinkedList
Convert a BST to a sorted circular doubly-linked list in-place. Think of the left and right pointers as synonymous to the previous and next pointers in a doubly-linked list.
Let's take the following BST as an example, it may help you understand the problem better:
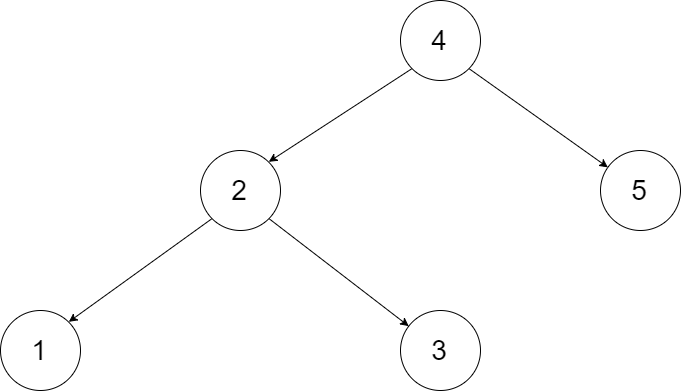
We want to transform this BST into a circular doubly linked list. Each node in a doubly linked list has a predecessor and successor. For a circular doubly linked list, the predecessor of the first element is the last element, and the successor of the last element is the first element.
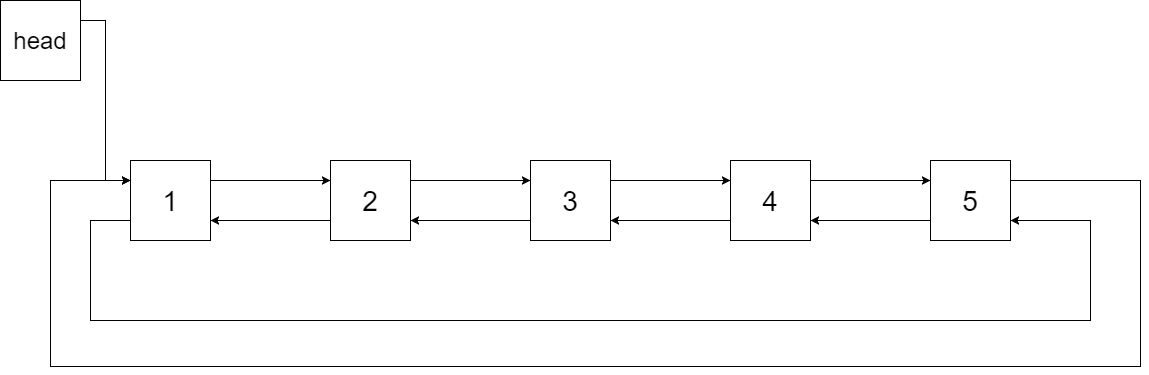
The figure below shows the circular doubly linked list for the BST above. The "head" symbol means the node it points to is the smallest element of the linked list.
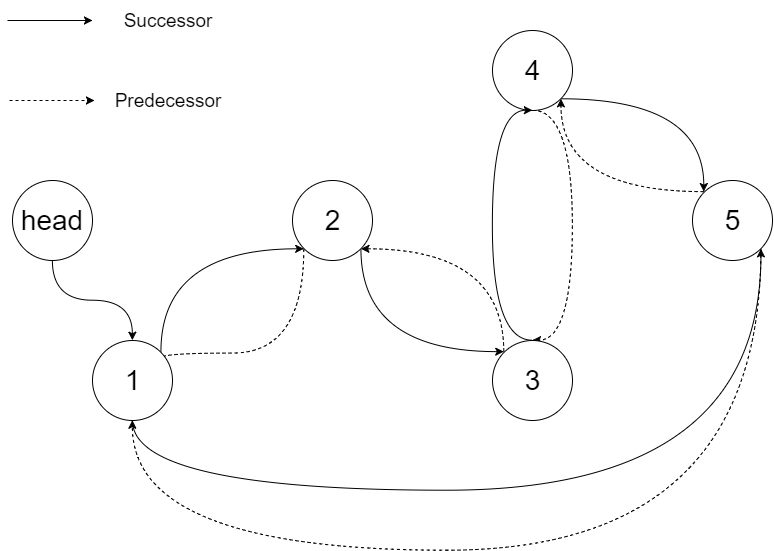
Specifically, we want to do the transformation in place. After the transformation, the left pointer of the tree node should point to its predecessor, and the right pointer should point to its successor. We should return the pointer to the first element of the linked list.
The figure below shows the transformed BST. The solid line indicates the successor relationship, while the dashed line means the predecessor relationship.
Note
递归
完全就是 in - order 的递归结构,左-中-右
核心在于 “中” 这步上,如何正确做好 “拼接” 工作
我们需要存一个全局变量 prev 用于保存 "左子树的最后一个节点",在每步上,和 root 做双向拼接; prev 初始化为 null;
额外用于遍历 LinkedList 还需要存下 head ; 在 prev 为 null 的时候 root 就代表着最左面的节点,设一下就好,之后就不用管了。
时间复杂度 O(n).
迭代
In-order 跑一遍,每次 pop 出来的时候,我们就有 root 了;
然后拼接的逻辑处理和递归的方法完全一样,这次连全局变量都不用,简单直接~
时间O(n),空间 O(log n)
Last updated